Why Repetitive Task Automation Matters for P&C Insurance Claims
Repetitive task automation uses technology to handle routine, manual, and time-consuming tasks without human intervention. For P&C insurance carriers, TPAs, and IA firms, this means automating activities like:
- Claims data entry from FNOL forms and documents
- Document classification for property, auto, pet, and workers' comp claims
- Status updates and notifications to claimants and adjusters
- Data validation and transfer between claims management systems
- Report generation for claim summaries and compliance
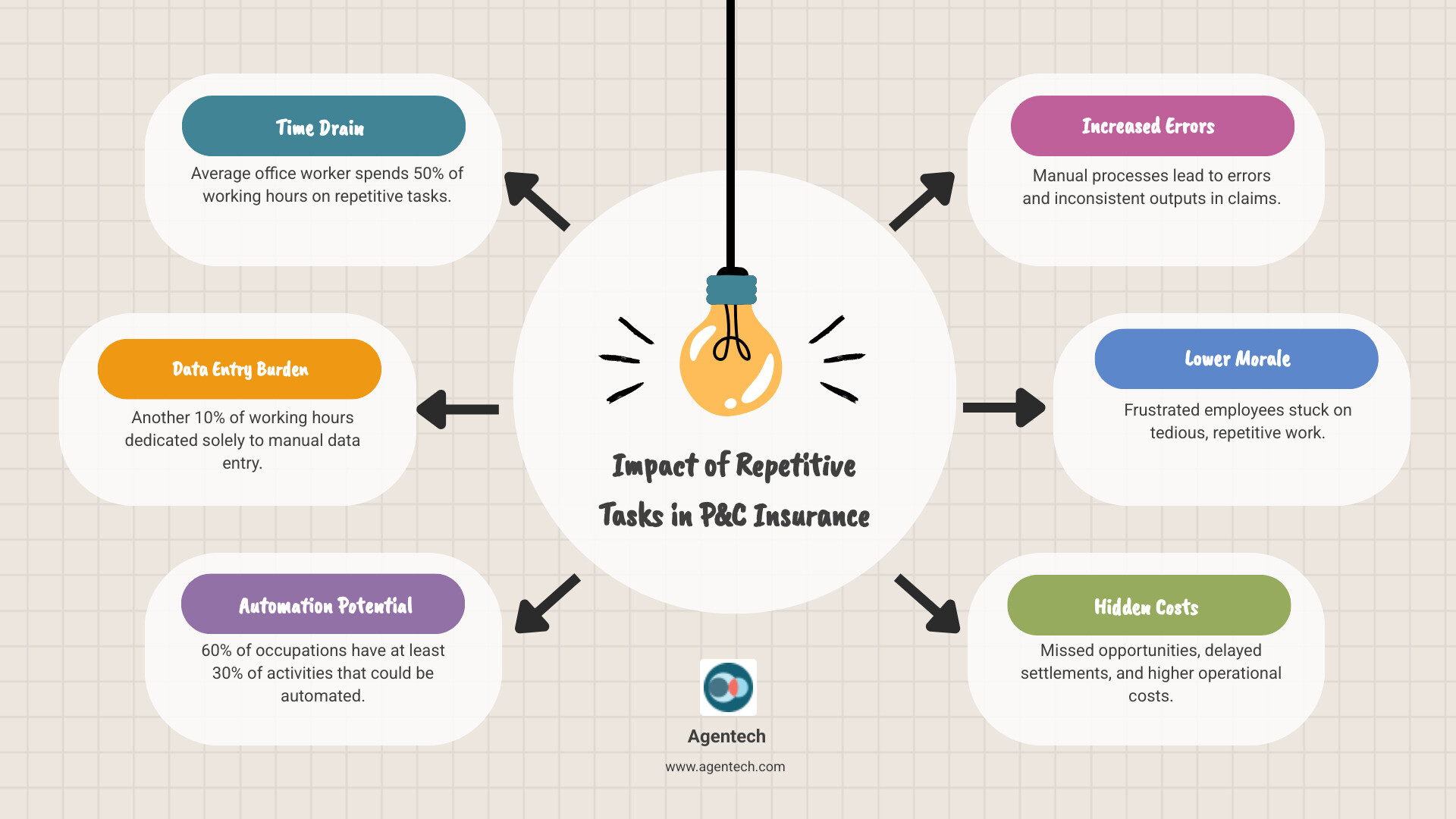
Office workers spend 50% of their hours on repetitive tasks, with 10% on manual data entry alone. For claims adjusters, this means hours spent on administrative work instead of evaluating claims and serving policyholders.
The cost goes beyond wasted time. Manual processes lead to errors, inconsistent results, and frustrated employees. McKinsey estimates that 60% of all occupations have at least 30% of their activities that could be automated. In P&C insurance claims, where data flows constantly, this opportunity is even greater.
When claims professionals are buried in data entry, they can't focus on investigating complex claims, negotiating settlements, and delivering exceptional service. This creates a hidden cost in delayed settlements and staff burnout.
Task automation transforms this. Instead of typing information from an ACORD form into your claims management software, automation extracts and transfers it instantly. Instead of manually routing claims, automation handles the assignment. The result? Claims teams reclaim their time for strategic work, processing speeds increase, error rates drop, and employee satisfaction rises.
I'm Alex Pezold, and I founded Agentech AI to revolutionize P&C insurance through AI-driven solutions. Repetitive task automation is the foundation of this change, enabling carriers and TPAs to process claims with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Understanding Task Automation: From Simple Scripts to Intelligent Systems
Task automation is the use of technology to perform routine tasks without human intervention. In P&C claims, this means using claims software and bots to automatically handle actions like transferring data, sending emails, or filling out forms within claims management software [1, 2]. Think of it as a digital assistant for the tedious chores.
Automation relies on predefined rules. A sequence of actions is programmed to execute when a specific trigger occurs. For example, when a new claim document arrives, automation can extract key information, classify the document, and route it to the correct claims adjuster. This seamless data movement between claims applications is a game changer. Automation can also monitor systems, flagging a claim if certain criteria are met or sending an alert for an approaching deadline, helping P&C organizations maintain smooth workflows [2].
The Evolution of Automation Technology
Automation technology has progressed through several key stages [15]:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in P&C insurance: The first generation, using bots to mimic human actions for simple, rule-based tasks like data entry. RPA struggles with unstructured data or system changes [15].
- Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) for claims: Adds machine learning to RPA, allowing it to handle more complex processes and recognize patterns, like extracting data from a standard ACORD loss notice form [15].
- Cognitive Process Automation (CPA) in property, auto, pet, and workers' comp: The newest frontier, using true AI to replicate human intelligence and learn on its own. CPA can assist with complex tasks in policy administration and underwriting, acting as "Digital Coworkers" [15]. We explore how AI Agents can revolutionize claims processing.
- The role of AI and machine learning in P&C claims automation: AI is the engine driving this evolution, allowing automation to understand context, process natural language, and analyze images to predict fraud or streamline damage assessment [1, 10]. Learn more about Machine Learning in Claims Processing.
Task Automation vs. Traditional Task Management
Task automation and traditional task management are fundamentally different. Traditional management often involves manual tracking and reactive workflows, where work waits for human handoffs. This approach relies on human effort and scales linearly with headcount.
In contrast, task automation uses technology to execute and complete tasks proactively, from start to finish [4]. For a claims team, the system automatically moves a claim to the next stage once conditions are met. This process-focused approach is highly scalable; an automated workflow can handle a massive increase in volume with minimal additional resources, making it ideal for growing P&C carriers and TPAs [4]. By handling repetitive steps, automation transforms claims task management into a streamlined, self-driving process, freeing professionals for more complex work.
The Business Case for Repetitive Task Automation
Why should P&C carriers, TPAs, and IA firms invest in repetitive task automation? The business case is compelling, offering benefits that directly impact the bottom line and employee well-being.
- Key benefits for P&C organizations: The primary advantages are increased efficiency, improved accuracy, significant cost savings, and higher employee satisfaction [4, 5].
- Increased efficiency and speed: Automation processes tasks much faster than humans, reducing claim cycle times and leading to quicker settlements. Our research shows teams using automation reduce human error and speed up delivery [5].
- Improved accuracy and compliance: Automation performs tasks with consistent accuracy, which is crucial in P&C claims where small errors have large financial or compliance consequences. Automated systems also ensure every step adheres to regulatory requirements [5].
- Significant cost savings: By reducing manual labor for routine tasks, organizations can cut operational costs. This optimizes resource allocation, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities and increasing capacity without adding headcount [4, 5]. We want to Reduce Administrative Burden.
- Improved employee satisfaction: Automating monotonous work reduces burnout and improves morale [5]. When employees are freed from "busywork" to focus on strategic and impactful tasks, job satisfaction and retention rates for claims professionals increase [4, 5].
Measuring the ROI of Your Automation Efforts
To understand the value of repetitive task automation, you must measure its impact with quantifiable results. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for P&C claims include [4, 5]:
- Time saved per claim: Quantify efficiency gains by tracking the reduction in processing time.
- Error rate reduction: Compare error rates of manual vs. automated processes to demonstrate improved accuracy.
- Employee satisfaction surveys: Gauge morale and satisfaction after implementing automation.
- Cost savings: Calculate the reduction in labor costs and expenses related to errors.
- Faster cycle times: Track the average time to close a claim before and after automation to see the impact on Efficient Claims Handling.
Supporting Modern Hybrid and Remote Work
Repetitive task automation is a critical enabler for maintaining efficiency in distributed work models. For remote claims teams, ensuring procedural consistency can be challenging, leading to communication gaps [5]. Automation provides a standardized way of executing tasks, guaranteeing that every claim process adheres to the same high standards, regardless of an employee's location [5]. It also reduces communication overhead by automating status updates and approvals, providing transparency that keeps everyone informed and reduces bottlenecks [5]. This is part of The Future of Work in Insurance: Embracing AI Agents as Digital Coworkers.
A 5 Step Guide to Implementing Automation
Implementing repetitive task automation is a strategic journey. For P&C carriers, TPAs, and IA firms, a structured approach is key. We recommend a 5-step framework, starting with gaining stakeholder buy-in from your claims team, IT, and leadership. Their support is essential for successful adoption [5].
Step 1 & 2: Identify and Assess Automation Opportunities
The journey begins with understanding where automation can provide the most value.
- Survey claims teams: Ask adjusters and support staff to identify tedious, time-consuming, and error-prone tasks. Their frontline insights are invaluable [4, 5].
- Observe daily P&C workflows: Watch claims processes directly to identify hidden inefficiencies and manual data transfers that could be automated [4].
- Identify bottlenecks: Look for points where claims get stuck. Streamlining these bottlenecks can have a ripple effect on overall efficiency.
- Assess task frequency and complexity: Prioritize tasks that are frequent, highly repetitive, and follow clear, rule-based logic. Avoid tasks requiring complex human judgment initially [4, 5].
- Prioritize high-impact tasks: Automating the initial data entry for First Notice of Loss (FNOL) forms is a high-impact, rule-based task. Another is automating the creation of the claim profile itself, a notoriously tedious task [4]. We made AI do this: Creating the Claim Profile.
Step 3, 4 & 5: Choose, Implement, and Optimize
Once you've identified opportunities, it's time to bring them to life.
- Explore automation solutions: Look for tools that are easy to use, integrate with your existing claims management systems, and can scale with your organization [4, 5]. Review various Insurance Automation Tools to find the right fit.
- Start with a pilot project: Begin with a small, manageable project with a clear, measurable outcome to test the automation and demonstrate early success before scaling [4, 5].
- Onboard and train adjusters: Provide thorough training and support. Explain how automation will benefit them by freeing up their time, and encourage feedback [4].
- Monitor performance metrics: Continuously track KPIs like time saved, error rates, and employee satisfaction to understand the real world impact [5].
- Gather user feedback: Listen to your claims team's insights to make adjustments and ensure the automation truly optimizes their workflows [5].
- Scale successful automations: Once a pilot proves successful, confidently expand it to other areas of your P&C operations.
Repetitive Task Automation in Action: Use Cases and Tools
Let's explore real world applications of repetitive task automation in Property & Casualty insurance and the tools that make it possible. For a comprehensive overview, see our guide on Automating Insurance Claims Processing.
Common Use Cases in P&C Insurance
- First Notice of Loss (FNOL) data entry: Automation extracts information from online forms, emails, or transcribed calls and automatically populates fields in your claims management software, eliminating manual entry.
- Automated claim profile creation: After FNOL, automation can gather all necessary initial data, verify policy details, and create a comprehensive claim profile without manual intervention.
- AI for Insurance Document Management: AI-powered automation can classify a deluge of documents (policy forms, medical records, repair estimates), extract key data, and store them in the correct digital folders, making them instantly searchable.
- Supporting claims adjudication: While final judgment remains human, automation streamlines the process by gathering relevant information, flagging discrepancies, and applying predefined rules for low-complexity claims, speeding up Automated Claims Adjudication Software.
The Role of AI in Modern Repetitive Task Automation
Artificial Intelligence is a powerful enabler for more sophisticated repetitive task automation in P&C insurance.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows machines to understand and interpret human language. In P&C, this means automated systems can process customer emails or chat transcripts to extract claim details or answer routine inquiries, freeing up adjusters for complex issues [1, 10]. Learn more about NLP applications in insurance.
- Computer Vision: This enables AI to interpret images. For property and auto claims, it can analyze photos of damage to assess severity or detect potential fraud. It can also extract data from scanned documents.
- Generative AI: This technology can create new content, such as summarizing lengthy claim notes, police reports, and medical documents into a concise overview for a supervisor. This dramatically reduces administrative time. We are seeing the true meaning of Agentic Meaning in these applications. For more details, see AI Applications in Insurance Claims Processing.
Essential Tools and Technologies
Effective repetitive task automation relies on the right tools:
- Low code platforms: These allow business users to create and customize automations with minimal coding.
- Integration tools: These allow different claims management software applications to communicate, enabling end to end automated workflows.
- Custom scripting with Python: For complex needs, scripting languages like Python offer flexibility to create custom bots for data analysis and workflow automation [9, 12]. The Python Software Foundation provides extensive resources for learning automation scripting.
- Specialized Core Insurance Software: Many modern core systems now include built-in automation capabilities or robust APIs for integration.
Overcoming Challenges and Looking to the Future
While repetitive task automation offers immense benefits, P&C carriers and TPAs must steer potential challenges for long term success. Common issues include employee resistance, poor data quality, the risk of creating brittle "automation debt," and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like CCPA and state-specific insurance laws [14]. Implementation can also fail if the complexity of existing processes is underestimated or the wrong tools are chosen.
Navigating the Pitfalls of Automation
Successfully implementing automation means proactively addressing these roadblocks.
- Overcoming resistance to change: Communicate clearly how automation benefits employees by freeing them from tedious tasks. Involve them in the process to foster ownership [4, 5].
- Ensuring data quality for AI: AI is only as good as its data. Invest in data cleansing and governance to ensure your claims data is accurate and reliable before automation.
- Avoiding "automation debt": Avoid quick, poorly designed automations that are hard to maintain. Build robust, scalable solutions to prevent them from becoming a future burden [5].
- Keeping a human in the loop: Use automation to augment, not replace, human judgment. Ensure a human can review, approve, or override automated actions for complex or critical decisions [4, 5].
- Adhering to regulatory guidance: The P&C insurance industry is heavily regulated. Ensure any automation complies with guidelines like the NAIC AI Model Guidance to keep processes transparent and fair.
The Future of Automation and the P&C Workforce
The future of repetitive task automation in P&C insurance promises a change of the workforce, not its replacement.
- The rise of digital coworkers: We are moving toward a future where AI-powered "Digital Coworkers" work alongside human claims professionals, handling data processing, document analysis, and routine communications with minimal maintenance [15].
- Shifting job roles: Claims professionals will transition from manual data entry to roles focused on strategic analysis, complex problem-solving, and customer relationship management.
- Augmenting adjuster capabilities: The goal is to empower adjusters, making them more efficient. By offloading monotonous tasks, automation allows them to focus on high value activities like investigating complex claims and applying their expertise. This is key to Solving the Insurance Labor Crisis with AI-Driven Innovation.
- The impact of continuously learning AI: As AI systems improve, the scope of automation will expand, continuously freeing up human potential and allowing P&C organizations to adapt with greater agility.
Conclusion
Repetitive task automation is no longer a luxury; it's a strategic imperative for P&C insurance carriers, TPAs, and IA firms. We've explored how automating these tedious to-dos can bring about remarkable benefits: increased efficiency and speed in claims processing, improved accuracy and compliance, and significant cost savings. Crucially, it also boosts employee morale and satisfaction, empowering claims professionals to focus on the high value, empathetic work they do best.
By understanding the evolution of automation from RPA to intelligent AI, and by following a structured implementation framework, P&C organizations can successfully integrate these technologies into their operations. While challenges exist, with careful planning, robust data governance, and a human centric approach to change management, these can be effectively steerd.
The future of claims processing involves a symbiotic relationship between human expertise and AI driven automation. We believe in augmenting adjuster capabilities, creating a workforce where digital coworkers handle the routine, allowing human professionals to excel in strategic analysis and customer service.
Ready to transform your claims processing and empower your team? Take the next step to streamline your operations with powerful AI Agents designed for the unique needs of P&C insurance.
Citations:
- AI for Task Automation. (n.d.). IBM.
- How automating repetitive tasks works. (n.d.). Dropbox.
- Find how to automate repetitive tasks. (n.d.). Asana.
- Saji, L. (2024, May 20). How to Automate Repetitive Tasks & Reclaim Your Team’s Time. Nimble.
- The best automated task management software. (2024, May 20). Motion.
- Managed IT Services & Co-Managed IT Services. (n.d.). Logically.
- Let your Mac do repetitive tasks for you. (n.d.). Apple Support.
- Let your Mac do repetitive tasks for you. (n.d.). Apple Support.
- Boost Python for Automation & Integrations. (n.d.). Robocorp.
- AI for Task Automation. (n.d.). IBM.
- Automation. (n.d.). Home Assistant.
- Sweigart, A. (n.d.). Automate the Boring Stuff with Python, Third Edition.
- Tasks 101. (n.d.). Regal.
- Workflow Orchestration. (n.d.). Roots Automation.
- The Evolution of Business Process Automation: From RPA to Digital Coworkers. (n.d.). Roots Automation.