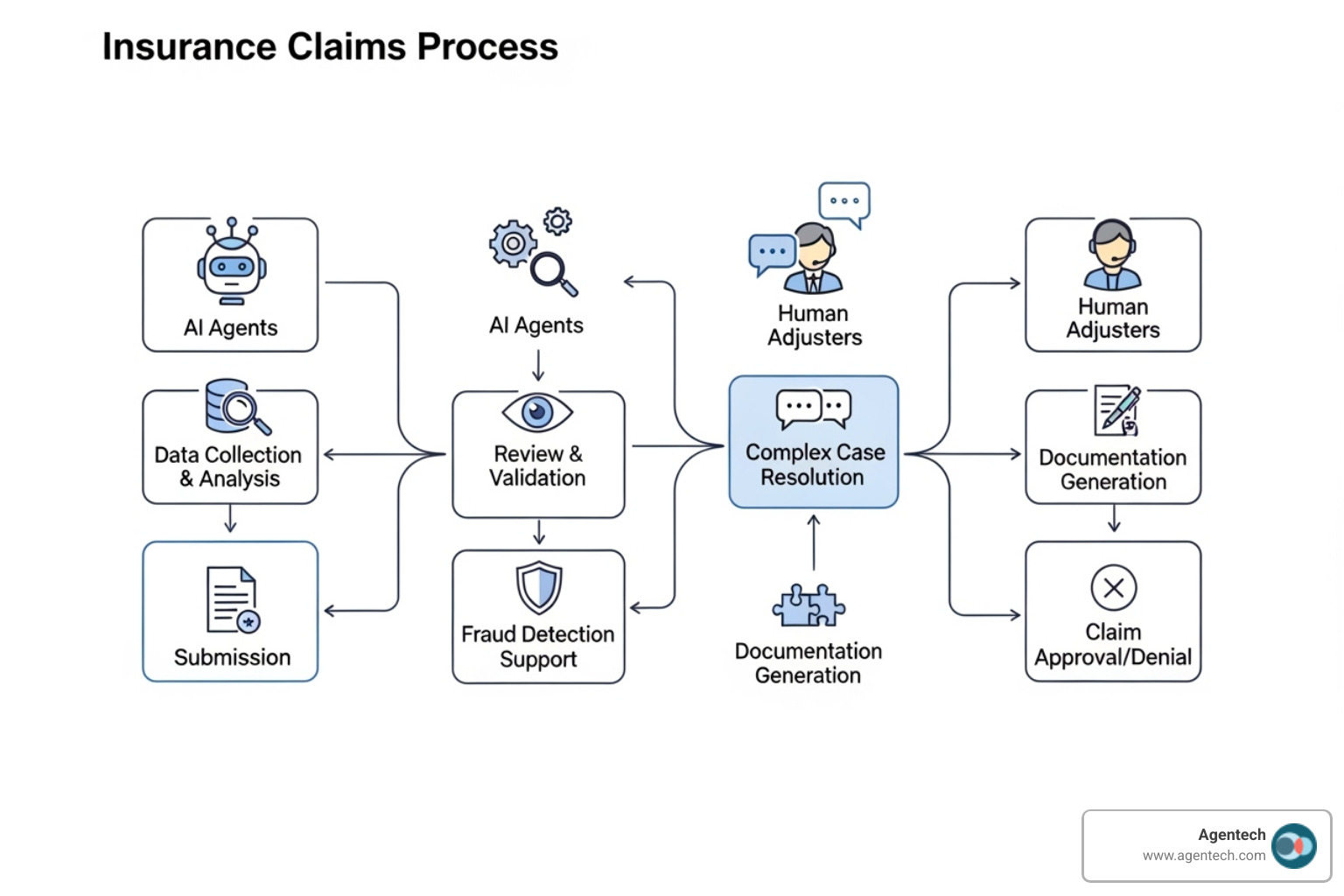
Moving Beyond Simple Automation in P&C Insurance Claims
Agentic AI frameworks represent a fundamental shift from traditional automation. Unlike simple rule-based systems, these frameworks allow AI agents to reason, plan, and act autonomously across multi-step workflows in Property & Casualty insurance claims. For claims managers, the promise is clear: AI agents that can handle First Notice of Loss (FNOL) intake, analyze vehicle damage reports, cross-reference policy details, and flag subrogation opportunities.
Quick Overview of Agentic AI Frameworks:
What they are: Foundational structures that enable AI agents to operate autonomously, make decisions, and collaborate on complex tasks without constant human intervention. Core components: Memory systems, reasoning engines, planning modules, and tool integration capabilities. Key difference: Unlike traditional automation, agentic systems can decompose complex claims tasks, adapt to new scenarios, and learn from feedback. Popular approaches: LangGraph, CrewAI, AutoGen, and Semantic Kernel offer different orchestration models. Primary benefit for P&C insurance: Dramatically reduce manual work and accelerate claim settlements while maintaining accuracy.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Research shows that while 61% of organizations have begun agentic AI development, 40% of deployments will be canceled by 2027 due to rising costs or unclear value. This statistic underscores why understanding these frameworks is critical before implementation.
The challenge lies in choosing the right foundation, as different frameworks take fundamentally different approaches to orchestration and agent collaboration. Understanding these differences helps you avoid the pitfalls that lead to canceled deployments.
I'm Alex Pezold, founder of Agentech AI. After successfully scaling and exiting TokenEx, I've focused on applying cutting-edge AI to solve the unique challenges of P&C insurance claims. We're building the AI workforce for P&C insurance by leveraging agentic AI frameworks to transform claims processing.
This guide breaks down what agentic AI frameworks do, how they differ from simpler automation, and what you need to know to implement them successfully in your claims operations. We'll focus on practical considerations for P&C insurance carriers, TPAs, and IA firms looking to reduce manual work and accelerate settlements.
The Anatomy of an Agentic AI Framework
Think of agentic AI frameworks as the nervous system for intelligent automation. Unlike traditional software that follows rigid scripts, these frameworks enable AI systems to be goal-driven. You give them an objective, like processing a First Notice of Loss, and they determine the steps needed to get there, adapting as circumstances change.
This capability is vital in Property & Casualty insurance, where claims workflows are rarely straightforward. An auto accident claim, for instance, requires verifying coverage, assessing damage, reviewing police reports, and determining liability. Agentic AI frameworks provide the architecture that lets AI agents handle these interconnected tasks intelligently.
We have a more detailed explanation of this concept at Agentic AI Definition.

Core Components and Functionalities
Every robust agentic AI framework is built on four essential components that mirror human problem-solving.
Memory exists in two forms. Short-term memory (context windows) allows an agent to recall immediate details within a single interaction, maintaining conversational coherence. Long-term memory uses vector databases to store and retrieve vast amounts of information, such as historical claims data, policy documents, and regulatory guidelines, to inform current decisions.
Reasoning is how agents think through problems. Chain-of-Thought prompting makes an agent break down complex issues into intermediate steps, providing transparency into its decision-making process. ReAct combines thought with action, allowing an agent to think, act, observe the result, and then decide the next step. This dynamic adaptation is essential for the unpredictable nature of claims processing.
Planning through task decomposition enables agents to tackle complex claims. A property damage claim is broken down into sub-tasks: collect the incident report, verify coverage, assess damage, estimate costs, and initiate payment. The planning module orchestrates these tasks in a logical, yet flexible, sequence.
Tools are functions or APIs that extend an agent's capabilities beyond processing text, allowing it to interact with your existing systems. An agent might use a tool to log a new claim in your claims management software, query a database for policyholder information, or integrate with third-party services for vehicle valuation.
Orchestration and Collaboration
The real change occurs when multiple agents collaborate on complex claims, which requires careful orchestration.
Centralized orchestration uses a manager agent to assign tasks to specialized agents, similar to a claims supervisor directing a team. This provides clear control over the workflow. Decentralized orchestration allows agents to interact more freely and coordinate directly, creating more flexible and resilient systems.
An architecture's design also impacts how agents handle long-running claims. Stateful orchestration maintains all information across steps, so an agent can pause and resume a claim over several days without losing context. Stateless orchestration treats each interaction as independent, which is simpler but less efficient for complex P&C insurance claims.
This collaborative approach streamlines claims processing in ways single-agent systems cannot. For example, on a complex auto claim, one agent can verify coverage while another analyzes damage photos and a third reviews police reports to determine liability. They communicate seamlessly, passing information between them using standardized protocols like FIPA's Agent Communication Language. This eliminates manual handoffs and allows human adjusters to focus on high-value judgment calls.
A Comparative Look at Open Source Agentic AI Approaches
The world of agentic AI frameworks has expanded rapidly, with numerous open-source options emerging [1]. This innovation provides many choices, but it also requires a clear understanding of what makes each framework unique. For P&C insurance claims, where accuracy and reliability are paramount, picking the right foundation is critical.
Frameworks differ in fundamental ways. Some prioritize ease of use for rapid prototyping, while others focus on production readiness for enterprise deployment. They also vary in how they orchestrate complex workflows and integrate with existing claims management software.

Comparing Key Approaches
When evaluating these frameworks for Property & Casualty insurance, we focus on what matters for claims operations: orchestration, memory management, ease of prototyping, and production readiness.
Here's how the major open-source agentic AI frameworks stack up:
| Framework | Orchestration Model | Memory Handling | Ease of Use for Prototyping | Production Readiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrewAI | Role-based, sequential/hierarchical "crews" | Short-term and long-term memory support built in [6] | Simplifies multi-agent orchestration [6] | Enterprise ready with optional integrations [6] |
| AutoGen | Flexible agent chat, configurable roles/workflows [5] | Requires external memory database for short/long-term [6] | Fast prototyping, highly flexible [6] | Requires external infrastructure for production [6] |
| LangGraph | Graph-based, function or graph-driven architectures [6] | Both short and long-term memory supported out of the box [6] | Easy to use for complex loops and state [6] | Fully production-ready [6] |
| Semantic Kernel | Experimental Agent Framework, Process Framework [5] | Relies on external memory components [5] | SDK for building generative AI apps [5] | Enterprise-grade from Microsoft [5] |
| Akka | Workflow engine, dynamic orchestration [6] | Native memory modules [6] | SDKs, composable components [6] | Production-ready, distributed [6] |
| OpenAI Swarm | Minimalist, agents and handoffs [3] | Short-term built-in, SQLite for long-term [6] | Fully featured SDK, early stage [6] | Hosted by OpenAI, still early [6] |
Understanding these trade-offs helps you avoid choosing a framework that's great for demos but struggles in production.
Architectural and State Management Differences
The architecture you choose shapes how your AI agents handle real-world claims. Two major approaches dominate the landscape.
Graph-based architectures, used by frameworks like LangGraph, treat your workflow as a series of connected nodes [5, 6]. This design is incredibly flexible, allowing for loops and branching logic, which is invaluable for claims that don't follow a linear path.
Role-based architectures, seen in CrewAI, organize agents into "crews" with specific roles [5, 6]. One agent might handle policy verification, another damage assessment. This approach mirrors human claims departments, making it intuitive to design.
State management is equally important for P&C insurance claims, which can unfold over days or weeks. Stateful design means the framework remembers a claim's entire history, allowing an agent to pick up exactly where it left off. This is crucial for long-running processes. Stateless design treats each interaction independently, requiring context to be re-injected each time. This is simpler but less suitable for the context-heavy work of claims processing.
We regularly consult resources like AWS Prescriptive Guidance on Agentic AI to stay current with architectural best practices.
Practical Applications and Strategic Selection for P&C Insurance
Agentic AI frameworks are practical tools that can transform how Property & Casualty insurance carriers, TPAs, and Independent Adjusting firms handle claims. The business benefits are measurable: slashing time spent on repetitive data entry, accelerating settlements, and freeing up your team to focus on complex problem-solving and empathetic policyholder interactions.
At Agentech, our AI agents handle the administrative grind so your adjusters can perform the meaningful work that requires human expertise.
Real-World Use Cases in Claims Processing
Here is what these frameworks can do in your claims operation:
- Automating First Notice of Loss (FNOL): An AI agent can guide policyholders through the entire FNOL process, collecting details, verifying policy information, and logging the claim into your claims management software. It can handle straightforward claims end-to-end and intelligently route complex cases to a human adjuster with a pre-populated file.
- Streamlining Subrogation and Liability Analysis: An AI agent can analyze police reports, witness statements, and accident diagrams to spot subrogation opportunities and provide preliminary liability assessments, saving countless hours of manual work.
- Analyzing Vehicle Damage Reports: For auto claims, agents can process damage photos and repair estimates in seconds. They cross-reference these against standard costs, flag discrepancies, and suggest optimal repair facilities.
- Cross-Referencing Policy Details: Agents rapidly access policy terms and endorsements to match them against incident details, instantly confirming eligibility or highlighting potential coverage gaps.
We've written extensively about these changes at How AI is transforming claims processing.
Choosing the Right Framework for Your P&C Insurance Needs
Selecting an agentic AI framework depends on your specific operational needs and existing technology. Key factors include:
- Scalability: Your framework must handle claim volume spikes, especially during catastrophic events, without performance degradation.
- Security and Data Privacy: The framework must offer robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations like SOC2, CCPA, and GDPR.
- Integration: It needs flexible APIs and connectors to your existing claims management software, policy administration systems, and other enterprise tools.
- Governance and Risk Management: You need tools to monitor agent behavior, detect anomalies, and ensure agents operate within defined boundaries to prevent unintended actions.
Navigating Implementation Challenges
Understanding obstacles upfront is key to success. A sobering fact: 40% of agentic AI deployments will be canceled by 2027 due to rising costs or unclear value. This is often a planning problem, not a technology one.
Success requires careful planning for implementation costs and ROI, starting with specific, measurable business objectives. It also involves addressing ethical considerations and building trust with adjusters by demonstrating how AI augments their capabilities rather than threatening their jobs. Fair, unbiased agent behavior is essential for gaining both adjuster buy-in and policyholder trust.
The path forward involves embracing AI agents as digital coworkers, a vision we explore at Embracing AI agents as digital coworkers.
Frequently Asked Questions about Agentic AI
As we explore agentic AI frameworks in the context of P&C insurance claims, certain questions come up repeatedly. Let's address the most common ones.
What is the main difference between an agentic framework and an AI agent builder?
Think of an agentic framework as a professional toolkit for developers. It provides the foundational components to build sophisticated, custom AI systems where multiple agents can collaborate on complex workflows [3]. We use these frameworks at Agentech for the control and flexibility needed for enterprise-scale P&C insurance claims processing.
An AI agent builder is a user-friendly platform designed for speed and simplicity. It allows users to quickly assemble and deploy agents for specific tasks, often with a visual interface and without deep coding knowledge [3]. Frameworks provide the underlying power, while builders focus on ease of deployment for more targeted applications.
How do agentic AI frameworks handle memory and learning?
Agentic AI frameworks handle memory and learning through several mechanisms that separate them from simple chatbots.
- Short-term memory uses context windows to remember what was just discussed in an interaction, ensuring a coherent conversation [7].
- Long-term memory is typically powered by vector databases, allowing agents to store and retrieve vast amounts of information across sessions, such as claims histories or policy documents [7].
- Learning from feedback is a key feature. Advanced systems analyze the results of their actions and incorporate feedback from adjusters to improve over time [7, 8]. For example, an agent can learn to request specific documents earlier in a claims process to prevent delays.
What are the biggest security risks with autonomous AI agents?
In P&C insurance, autonomous AI agents handle sensitive information, so mitigating security risks is critical.
- Prompt injection attacks occur when a user manipulates an agent's behavior with crafted prompts to override its instructions or extract confidential data [4].
- Data leakage is a concern when agents access sensitive claims data. Without proper safeguards, an agent might unintentionally expose private information [4].
- Unintended actions can happen if an agent operates without clear constraints, such as sending incorrect communications or making decisions outside its scope [4, 7].
To counter these risks, we emphasize human-in-the-loop oversight and robust guardrails [6]. Human judgment remains essential for high-stakes decisions. Our systems are designed so adjusters can review and approve critical agent actions, while guardrails provide predefined rules to prevent agents from operating outside their intended parameters.
The Future is Agentic: Changing P&C Insurance Operations
We are at a turning point in P&C insurance claims processing. Agentic AI frameworks are fundamentally reshaping what is possible by combining human expertise with AI capabilities. The benefits, including increased efficiency, faster settlements, and improved decision-making for adjusters, are already being realized by forward-thinking carriers, TPAs, and Independent Adjusting firms.
AI agents have evolved into digital coworkers, handling the repetitive administrative tasks that consume adjuster time. This allows your team to focus on what truly matters: complex liability determinations, empathetic policyholder conversations, and strategic decisions. We have discussed this shift toward embracing AI agents as digital coworkers in depth.
Building these systems is complex, and as statistics show, many deployments fail due to underestimating the challenges. That is why we built Agentech. We harness agentic AI frameworks specifically for P&C insurance, navigating the technical complexity for you. Our solutions are designed for the unique workflows of residential property, auto, pet, and workers' compensation claims, with a focus on security, governance, and seamless integration.
The future of P&C insurance operations is not about replacing humans with AI. It is about combining both to make claims processing faster, more accurate, and more satisfying for everyone. For policyholders who get faster settlements, for adjusters who can focus on meaningful work, and for carriers who can improve quality and efficiency.
Find out how our AI Agents can revolutionize your claims operations.
Citations:
[1] Silfverskiöld, I. "Agentic AI: Comparing New Open-Source Frameworks" - Data Science Collective, Medium
[2] "Agentic AI frameworks, protocols, and tools on AWS" - AWS Prescriptive Guidance
[3] "Agentic Frameworks: The Complete Guide to the Systems Used in Building Autonomous Agents" - Moveworks Blog
[4] "New capabilities in Azure AI Foundry and Microsoft Agent Framework" - Microsoft Azure Blog
[5] "AI agent frameworks: Choosing the right foundation for your business" - IBM Developer
[6] "Agentic AI frameworks for enterprise scale: A 2025 guide" - Akka.io
[7] Palod, P. "Exploring the Agentic Framework in AI" - Medium
[8] Arsanjani, A. "A Framework for Improved Agentic AI: Smarter, Safer, and Scalable Systems" - Medium