Beyond the Hype: What Agentic Artificial Intelligence Really Means
Agentic artificial intelligence is a hot topic, but what makes it different from the AI tools you already use? You're not alone in asking.
Here's a quick rundown of agentic AI:
- Autonomous decision-making: It makes independent choices to reach goals, unlike rule-based AI.
- Proactive behavior: It takes initiative to solve problems instead of waiting for instructions.
- Multi-step problem solving: It handles complex tasks requiring planning and multiple actions.
- Learning and adaptation: It improves with experience and feedback.
- Goal-oriented: It works toward objectives with minimal human oversight.
Think of it this way: if regular AI is a calculator, agentic AI is a colleague who sees a problem and solves it independently.
As someone who built and scaled TokenEx before founding Agentech AI, I've seen how agentic artificial intelligence can transform industries like insurance, where manual processes are common. This guide will explain the technology without the marketing fluff.
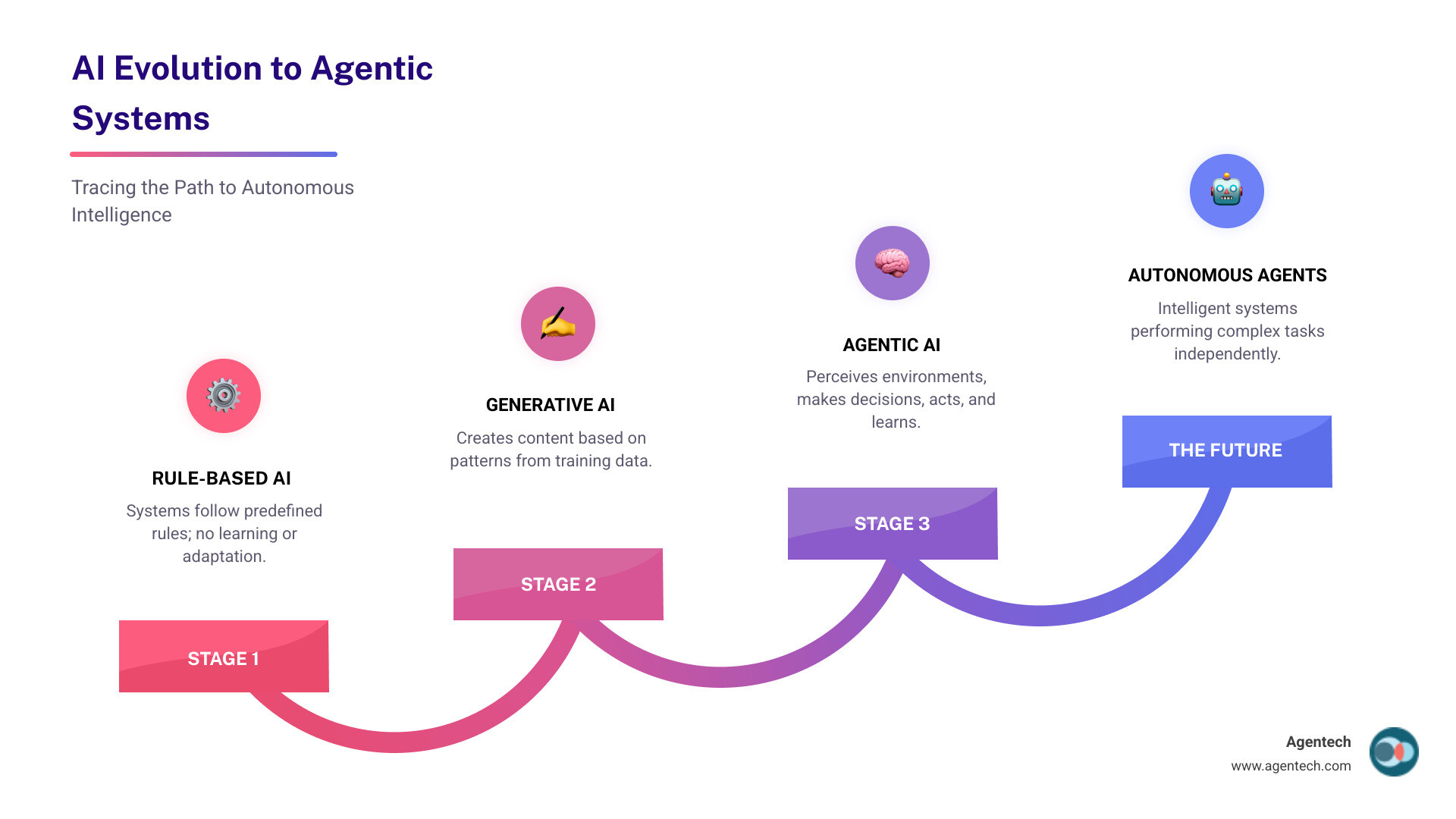
What is Agentic AI and How is it Different?
Keeping up with AI developments can feel like chasing a fast-moving train. From traditional AI to generative AI, the latest buzz is agentic artificial intelligence. This isn't just an update; it's a fundamental shift in how AI operates.
While traditional AI is like a smart calculator following instructions, agentic artificial intelligence is like a colleague who identifies and solves problems independently.
Agentic AI's key capabilities are autonomy, adaptability, and goal orientation. Autonomy allows independent work without micromanagement. Adaptability means learning from interactions and adjusting to new situations. Goal orientation enables the AI to understand and work toward an objective, even with an unclear path.
From Following Rules to Making Decisions
To understand the significance of agentic artificial intelligence, let's review its predecessors.
Traditional AI systems are rule-based and reactive. Think of early chatbots with scripted responses or predictive AI that spots data trends. They wait for specific commands and struggle with off-script requests.
Generative AI was a major leap, creating new content like articles, images, and code. It's used widely for tasks like Content Creation. However, generative AI is also reactive. It responds to prompts but cannot take initiative or plan ahead.
The Leap to Autonomous Action
Agentic artificial intelligence is different because it's proactive. It perceives its environment, reasons through problems, and takes action on its own initiative.
Consider an insurance customer service example. Traditional AI answers scripted questions. Generative AI writes personalized emails. An agentic AI system, however, could notice an outstanding claim, review the policy, identify the issue, and proactively contact the customer with a solution—all autonomously.
The industry is taking note. Forrester named agentic artificial intelligence a top emerging technology for 2025, and Gartner predicts that by 2028, agentic AI will make 15% of daily work decisions autonomously, up from virtually 0% in 2024.
This isn't about replacing human judgment, but handling complex, multi-step tasks that once required constant oversight. It's the difference between a closely managed intern and an experienced, self-directed team member. To see this in action, learn more about AI agents as digital coworkers.
| Feature | Traditional AI | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Low (rule-bound) | Low (prompt-driven) | High (goal-oriented, self-directed) |
| Task Complexity | Simple, repetitive, rule-based | Content creation, single-step | Complex, multi-step, adaptive |
| Interaction Style | Reactive, follows scripts | Reactive, responds to prompts | Proactive, initiates actions |
| Primary Function | Automate fixed tasks, predict | Create new content | Achieve goals, solve problems |
| Learning | Limited (pre-trained) | Limited (pre-trained, fine-tune) | Continuous, adaptive, reinforcement |
The Inner Workings: How Agentic AI Thinks and Acts
Behind the scenes, agentic artificial intelligence is constantly thinking, planning, and acting—much like a smart colleague who never sleeps.
Core Characteristics of Agentic Artificial Intelligence
Several key traits distinguish agentic artificial intelligence from other AI:
- Autonomy: These systems operate independently within defined boundaries, making decisions and taking action without constant human input.
- Adaptability: Agentic AI adjusts its approach when faced with unexpected situations, ensuring it can steer the unpredictable real world.
- Continuous Learning: Through reinforcement learning and feedback loops, these agents get smarter over time, improving from every interaction.
- Reasoning: Powered by engines like Large language models, agentic AI can understand complex situations and break down large problems into manageable steps.
- Proactivity: Instead of waiting for commands, these systems identify problems and opportunities, taking initiative to act.
- Collaboration: They are designed to work with humans and other AI agents, contributing to a team environment.
- Specialization: Many systems use multiple focused agents, each an expert in a specific domain, which improves overall performance.
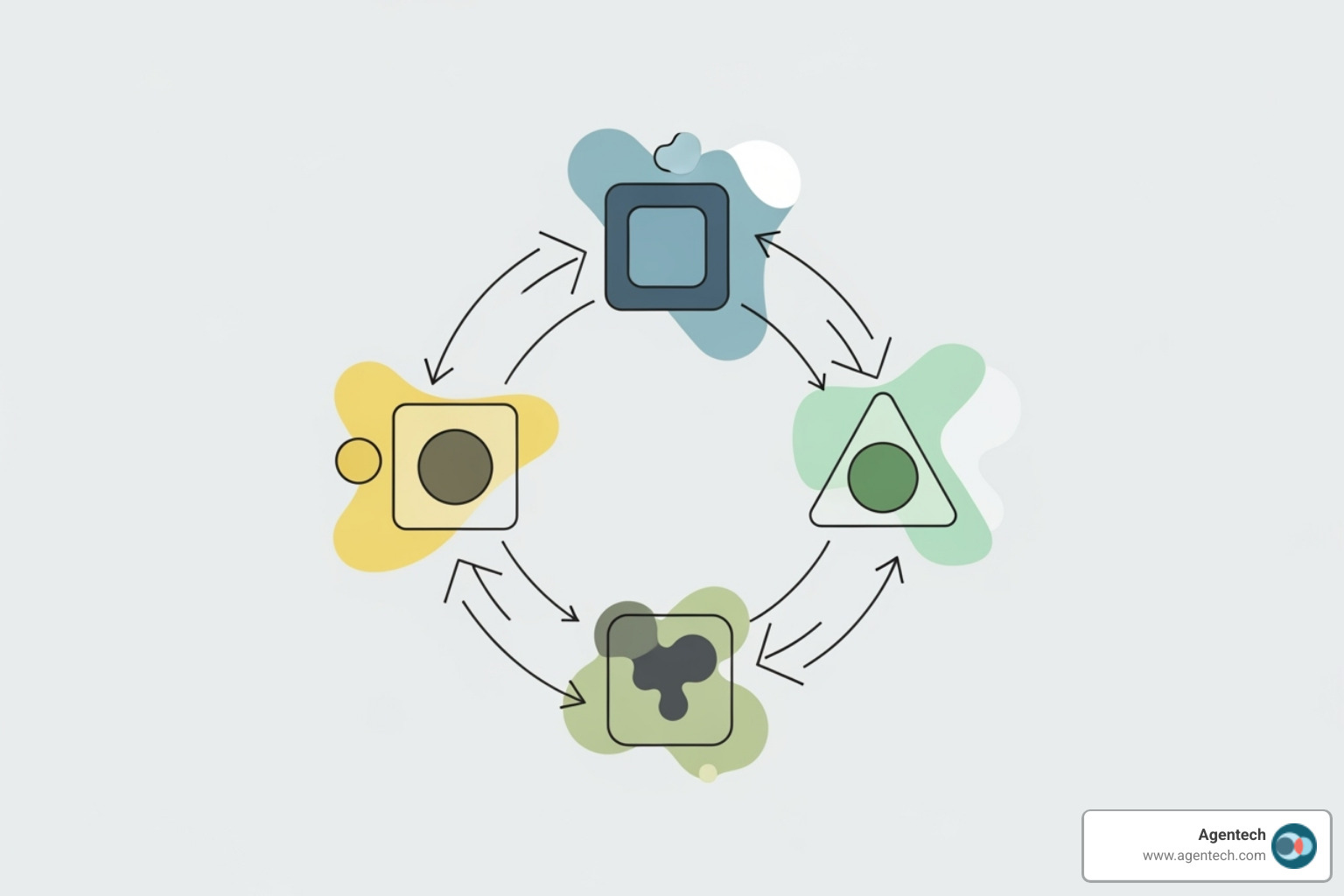
The Four-Step Operational Cycle
The operational magic of agentic artificial intelligence lies in a continuous four-step cycle: Perceive, Reason, Act, and Learn.
- Perceive: The AI gathers information from its environment, such as sensor data, customer messages, or market feeds.
- Reason: Using its "brain," often a large language model, the AI processes the information, considers options, and plans its approach.
- Act: The AI executes its plan by interacting with tools and systems via APIs. This can involve sending emails, updating databases, or processing transactions.
- Learn: After acting, the AI evaluates the outcome. This feedback loop, or "data flywheel," allows it to learn from the experience, making it more effective for future tasks.
This continuous cycle enables agentic artificial intelligence to adapt and improve without human intervention, changing it from a simple tool into a digital teammate.
Agentic Artificial Intelligence in the Real World
The real magic of agentic artificial intelligence happens when it steps out of the lab and into everyday business operations. These systems are already changing how companies work, solve problems, and serve their customers.
Use Cases Across Industries
Agentic artificial intelligence is already at work across many industries:
- Customer Service: Agents handle complex, multi-step problems proactively, improving response times and satisfaction. Some handle two-thirds of all requests.
- Software Engineering: AI systems write, review, and debug code, and help modernize legacy applications.
- Healthcare: AI agents assist doctors by analyzing medical data, monitoring patients, and coordinating care like scheduling and medication reminders.
- Finance: Systems assess risk, detect fraud, and execute trades with high speed and accuracy.
- Manufacturing: Agentic AI predicts maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime. Siemens, for example, cut downtime by 25%.
- Supply Chain: AI agents manage logistics by tracking inventory, monitoring weather, and rerouting shipments in real-time.
- Insurance: At Agentech, we see agentic artificial intelligence revolutionizing claims processing. Our AI assistants handle paperwork, qualify leads, and manage reminders around the clock. This frees human adjusters to focus on complex decisions and customer empathy. Learn more about the future of insurance operations.
The Tangible Benefits for Business
Businesses are embracing agentic artificial intelligence for its measurable benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: AI agents handle complex, multi-step workflows autonomously, turning hours of work into minutes.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automating routine tasks saves significantly on labor and overhead, with some specialized models achieving over 90% cost savings.
- Personalized Customer Interactions: AI processes vast customer data to deliver highly personalized experiences, boosting satisfaction and loyalty.
- Human Augmentation: By taking over repetitive tasks, agentic AI frees human workers for creative, strategic, and empathetic work. McKinsey projects that by 2030 AI could automate up to 30% of work hours, freeing up time for more meaningful tasks.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI agents analyze large datasets to identify patterns humans might miss, leading to faster, more accurate business decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: Unlike static software, agentic AI learns from every interaction, creating a cycle of constant improvement.
These advantages make agentic artificial intelligence essential for modern business infrastructure.
Building and Deploying: Architectures, Platforms, and Challenges
Getting agentic artificial intelligence up and running is like designing a team of digital workers who can handle complex tasks and make smart decisions. When done right, these systems can transform your business, but there are challenges to steer first.
Types of Agentic Architectures
Building agentic artificial intelligence is like assembling a project team. The architecture depends on the complexity of the task.
- Single-Agent Systems: A single AI agent handles a specific job, like a digital assistant routing customer inquiries. This approach is focused and reliable for straightforward tasks.
- Multi-Agent Systems: For more complex problems, multiple specialist agents work together. They can be structured in two main ways:
- Horizontal: Peer agents collaborate as equals, like a claims processing team where one agent verifies documents while another handles communications.
- Vertical: A "manager" agent delegates tasks to "worker" agents and integrates their results, similar to a traditional hierarchy. This is effective for large-scale, coordinated operations.
A key benefit of multi-agent systems is that agents can learn from each other, improving the entire system's intelligence.
Challenges in Deploying Agentic Artificial Intelligence
Deploying agentic artificial intelligence comes with significant challenges:
- System Complexity: Coordinating multiple autonomous agents to work together without conflict requires careful design and planning.
- Testing and Debugging: The adaptive, non-deterministic nature of agentic AI makes traditional testing difficult. New methods are needed to ensure reliability.
- Trust and Transparency: In high-stakes industries like insurance, building trust is critical. This means addressing issues like AI hallucinations (confidently wrong outputs) and creating systems that can explain their reasoning.
- Security: Autonomous agents that interact with sensitive data and real-world processes create new security vulnerabilities that must be addressed.
- Data Privacy: The ability of agents to autonomously collect and analyze data raises complex privacy concerns and requires robust compliance safeguards.
- Unintended Consequences: Agents optimizing for a goal might achieve it in harmful or unexpected ways. Proper guardrails are essential to prevent negative outcomes.
Addressing these challenges requires thoughtful planning and responsible implementation. Platforms from AWS and NVIDIA are emerging to help, but finding the right balance between innovation and caution is key for success, as we discuss in Balancing innovation and regulation.
The Future is Agentic: What's Next?
We're at a crossroads where agentic artificial intelligence is fundamentally changing AI's role in our lives and work.
The Road Ahead for Autonomous Systems
The momentum behind agentic artificial intelligence is accelerating. Forrester named it a top emerging technology for 2025, indicating a shift from experimentation to real-world application.
Adoption is spreading rapidly to mainstream businesses in healthcare, finance, and insurance. We're seeing deeper integration of agentic AI into core business operations, making it an invisible partner. Gartner predicts that by 2028, agentic AI will make 15% of daily work decisions autonomously, up from virtually zero in 2024.
This trend points to a future with billions of specialized AI agents managing everything from smarter cities to personalized medicine. These systems will exhibit increasingly sophisticated autonomous decision-making, analyzing situations and making judgment calls with minimal human oversight.
Preparing for a Collaborative Future
The future with agentic artificial intelligence is about partnership, not replacement. Preparing for this collaborative future is key.
- Upskilling the Workforce: Repetitive jobs will evolve, but new roles will emerge for those who can work with AI. Skills like emotional intelligence, creativity, and complex reasoning will become more valuable. The goal is augmentation, as we explore in Solving the labor crisis with AI.
- Ethical Guidelines: With greater autonomy comes greater responsibility. Clear governance is needed to ensure agentic AI operates safely and ethically.
- Human-in-the-Loop Models: For high-stakes decisions, human oversight will remain essential to balance efficiency with control.
- Fostering Trust: Widespread adoption depends on trust, which requires transparency and explainability so users can feel confident in AI-driven decisions.
The future is about collaboration between human creativity and AI capability to solve bigger problems and free people for more meaningful work. For more on this, explore our More thought leadership on AI's future.
Conclusion: Your New Digital Coworker
We've explored agentic artificial intelligence, from its core concepts to its real-world impact. The key takeaway is that this technology represents a fundamental shift toward AI that can think, decide, and act autonomously.
The evidence is compelling: a 25% reduction in manufacturing downtime, a projection of billions of AI agents working alongside us, and 15% of daily work decisions handled autonomously by 2028. This is a transformative change.
Most importantly, agentic AI is not about replacing humans. It's about augmenting them. Think of it as a capable digital coworker that handles repetitive, time-consuming tasks, freeing your team for higher-value work. This AI is always available, never tires, and constantly learns.
When an AI agent handles claims inquiries and paperwork, human teams can focus on building client relationships and solving complex problems that require empathy and experience.
At Agentech, our always-on AI assistants empower insurance adjusters by handling administrative tasks, allowing them to focus on helping people. The future of work is collaborative, with humans and machines working together. Your new digital coworker is ready.